General Dermatology | Melanoma
Melanoma comes from skin cells called melanocytes. These cells produce melanin, the dark pigment that gives our skin its color. Most melanomas are black or brown in color, but some are pink, red, purple or skin-colored.
Any area of the body can be affected by melanoma, with about 30% of melanomas beginning in an existing mole on your body and the rest appearing on normal skin. Melanoma accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, but is responsible for the majority of skin cancer-related deaths.
Knowing how to spot melanoma early is important because when spotted early, melanomas are highly treatable.
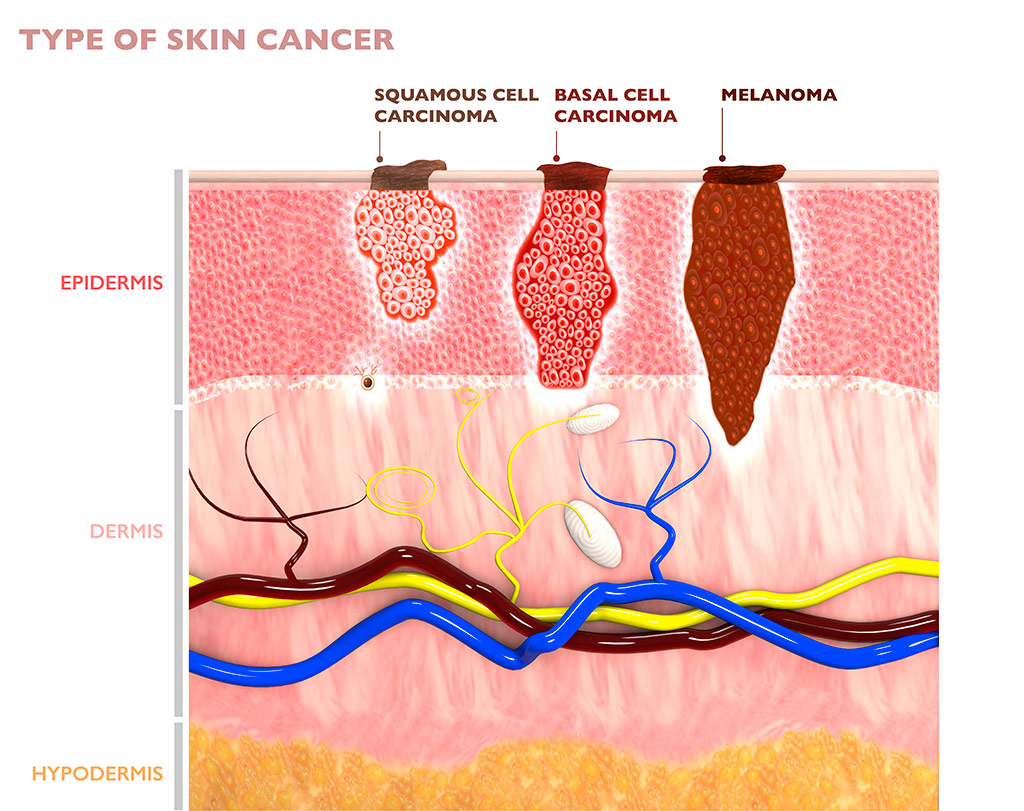
Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
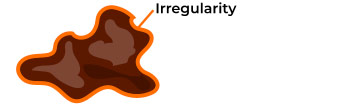
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s ABCDE rules for detecting melanoma when you’re just not sure about a spot on your skin.
Use this ABCDE chart below to help you quickly and more easily identify any changes in your moles and make an appointment to see our team.
When half of the mole does not match the other half

When the border (edges) of the mole are ragged or irregular
When the color of the mole varies throughout

If the mole’s diameter is larger than a pencil’s eraser

Changes in the way the mole looks over time
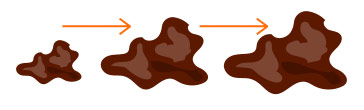
Please schedule an appointment to have any spots you think just don’t look or feel right. And remember, all melanomas do not fit the ABCDE rule, so let us know about anything unusual or changes in any existing moles.
Most experts agree that one of the major risk factors for melanoma is sun exposure, especially sunburns in youth. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from tanning beds also increases your risk of melanoma and has been designated as cancer causing by the World Health Organization.
Risk factors
Although anyone can develop melanoma, those at an increased risk have:
Diagnosing Melanoma Carcinoma
In order to determine if you have skin cancer, our team will perform a comprehensive skin exam, checking for bumps or spots that look abnormal in color, size, shape or texture.
Our team will also review your medical history and ask you about:
Following the exam, if we think your spot should be evaluated further, we will biopsy the spot and send the tissue sample to our dermatopathology lab where our pathologist will examine it. If cancer is found, your doctor will discuss the different options you will have for treating the melanoma.
Surgery is generally the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office.
In the early stages of melanoma, surgery has a high probability of curing the melanoma. However more advanced cases may require other types of treatments, like chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy.
We are proud to have received this distinction for our service to the military.

Privacy Policy | ©2024 Southeastern Dermatology Group, P.A. All Rights Reserved. Dermatology Solutions Group, LLC